What Are All The Organelles In A Animal Cell
Nosotros are enlightened of the fact that the cell is the structural and fundamental unit of measurement of life. It is as well the smallest and the most basic biological unit of living organisms. On the basis of the cellular organization, cells are further classified as eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Found cells and animal cells fall under the eukaryotic category.
Table of Contents
- Definition
- Explanation
- Diagram
- Construction
- Types
- Conclusion
Let the states have a detailed overview of the animal prison cell, its types, diagram and structure.
Fauna Cell Definition
"An animal cell is a type of eukaryotic jail cell that lacks a cell wall and has a true, membrane-bound nucleus along with other cellular organelles."
Caption
Animal cells range in size from a few microscopic microns to a few millimetres. The largest known animal cell is the ostrich egg, which can stretch over 5.1 inches across and weighs about i.iv kilograms. This is in stark contrast to the neuron in the human being body, which is but 100 microns beyond.
The shape of animal cells also varies, with some being flat, others oval or rod-shaped. There are also more intriguing shapes such as curved, spherical, concave and rectangular. Most of the cells are microscopic in size and can only be seen under the microscope.
As stated earlier, animal cells are eukaryotic cells with a membrane-leap nucleus. Furthermore, these cells exhibit the presence of DNA inside the nucleus. They also contain other membrane-bound organelles and cellular structures which behave out specific functions necessary for a cell to office properly.
Animal Cell Diagram
The diagram given beneath depicts the structural organization of the brute jail cell. The various jail cell organelles present in an fauna cell are conspicuously marked in the animal jail cell diagram provided beneath.
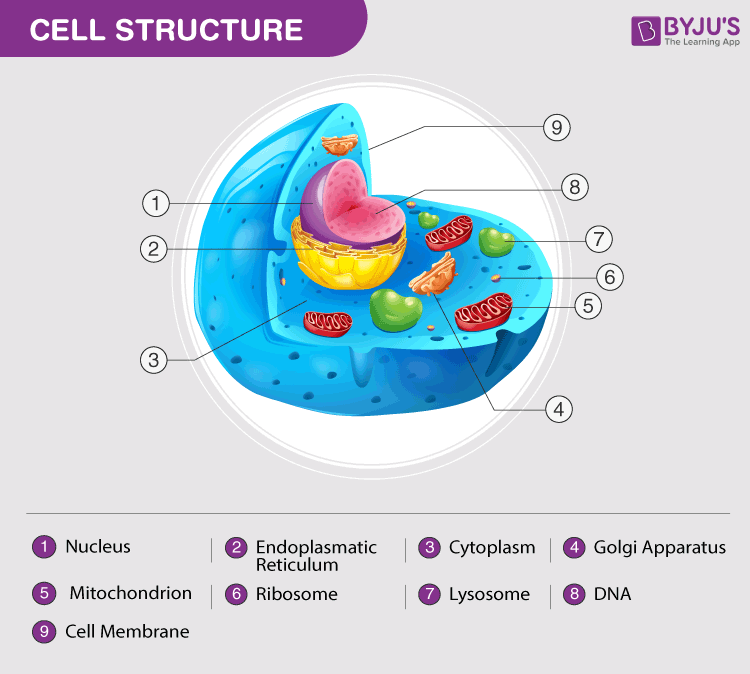
Animal cell diagram detailing the various organelles
Though this animal cell diagram is not representative of whatever one particular type of cell, it provides insight into the primary organelles and the intricate internal structure of well-nigh animal cells. Furthermore, it is easy to distinguish between a plant and brute cell diagram simply by inspecting the presence or absence of a cell wall.
Animal Cell Construction
Animate being cells are generally smaller than plant cells. Some other defining characteristic is its irregular shape. This is due to the absence of a cell wall. But animal cells share other cellular organelles with establish cells as both accept evolved from eukaryotic cells.
A typical beast cell comprises the following cell organelles:
Cell Membrane
A thin semipermeable membrane layer of lipids and proteins surrounding the prison cell. Its primary function is to protect the cell from its surrounding. Also, it controls the entry and exit of nutrients and other microscopic entities into the cell. For this reason, cell membranes are known equally semi-permeable or selectively permeable membranes.
Nucleus
It is an organelle that contains several other sub-organelles such as nucleolus, nucleosomes and chromatins. Information technology also contains DNA and other genetic materials.
Nuclear Membrane
It is a double-membrane construction that surrounds the nucleus. Information technology is also referred to equally the nuclear envelope.
Centrosome
It is a small organelle institute nigh the nucleus, which has a thick middle with radiating tubules. The centrosomes are where microtubules are produced.
Lysosome
They are circular organelles surrounded by a membrane and comprising digestive enzymes which help in digestion, excretion and in the cell renewal process.
Cytoplasm
A jelly-similar cloth which contains all the cell organelles, enclosed within the jail cell membrane. The substance constitute within the prison cell nucleus, contained by the nuclear membrane is called the nucleoplasm.
Golgi Appliance
A flat, smooth layered, sac-like organelle which is located near the nucleus and involved in manufacturing, storing, packing and transporting the particles throughout the cell.
Detailed Reading: Golgi Apparatus
Mitochondrion
They are spherical or rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. They are the powerhouse of a jail cell as they play an important role in releasing energy.
Ribosome
They are minor organelles fabricated upwardly of RNA-rich cytoplasmic granules, and they are the sites of protein synthesis.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
This cellular organelle is composed of a thin, winding network of bleary sacs originating from the nucleus.
Vacuole
A membrane-spring organelle present inside a jail cell involved in maintaining shape and storing water, food, wastes, etc.
Nucleopore
They are tiny holes present in the nuclear membrane which are involved in the movement of nucleic acids and proteins across the nuclear membrane.
Animal Cell Types
At that place are numerous types of animal cells, each designed to serve specific functions. The most common types of animal cells are:
Skin Cells
Melanocytes, keratinocytes, Merkel cells and Langerhans cells
Muscle Cells
Myocyte, Myosatellite cells, Tendon cells, Cardiac muscle cells
Blood Cells
Leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelet
Nerve Cells
Schwann cell, glial cells etc
Fat Cells
Adipocytes
Points to Note Virtually Brute Jail cell
The prison cell is the structural and functional unit of life. These cells differ in their shapes, sizes and their structure as they take to fulfil specific functions. Plant cells and animate being cells share some common features as both are eukaryotic cells.
However, they differ equally animals need to adapt to a more active and non-sedentary lifestyle. Furthermore, animals demand to acquire their ain nutrient, therefore, they do not possess any of the specialized cell organelles such as chloroplasts.
Animal Jail cell is a fundamental topic taught in class 9 and higher. To discover more information about the animal cell structure, its types, functions jail cell diagrams or other related topics, please explore BYJU'S Biology.
Further Reading :
- Cells
- Prokaryotic Cells
- Competent Cells
- Animal Tissue: Types and Structure
- Regeneration
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an animal cell?
As the name implies, an fauna cell is a type of cell that is seen specifically in animal tissues. It is characterized by the absence of a prison cell wall, with cell organelles enclosed inside the cell membrane.
Proper noun the prison cell organelle that contains the genetic material of the jail cell.
Which cell organelle is responsible for the generation of free energy for cellular activities?
Proper name the double-layered membrane responsible for enveloping the nucleus.
What is the role of lysosomes?
Lysosomes help in digestion, excretion and cell renewal process.
State the diverse types of animal cells.
- Skin Cells
- Musculus Cells
- Blood Cells
- Nerve cells
- Fat Cells
Explain how an creature cell varies from a plant cell.
An animal cell is usually irregular and circular in shape. This is primarily due to the absence of the jail cell wall, which is a characteristic feature of plant cells. Furthermore, animal cells do not accept plastids equally animals are not autotrophs.
Proper name the selectively permeable construction that envelopes the unabridged cell.
Which cell organelle is responsible for packing?
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/animal-cell/
Posted by: marincamonwarld.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Are All The Organelles In A Animal Cell"
Post a Comment